Hepatitis
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver, most commonly caused by a viral infection. There are five main hepatitis viruses that cause acute and/or chronic infection, referred to as types A, B, C, D and E. In particular, types B and C lead to chronic disease in hundreds of millions of people worldwide. In the WHO European Region an estimated 15 million people live with chronic hepatitis B, and an estimated 14 million people are infected with hepatitis C. Because the disease is often asymptomatic and left untreated, chronic hepatitis is a major cause of liver cirrhosis and primary liver cancer. People who inject drugs are particularly vulnerable to hepatitis and co-infection with both hepatitis and HIV is common.
Top story
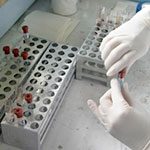
 Integrated screening for infectious diseases: a success story from Georgia
Integrated screening for infectious diseases: a success story from Georgia
Testing simultaneously for several infectious diseases in primary health care settings is feasible and can help to bring down the burden of chronic hepatitis C, HIV, sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and tuberculosis (TB) in countries in eastern Europe and central Asia, results from Georgia and elsewhere in the WHO European Region show.
Vaccination and COVID-19

- COVID-19 vaccines and vaccination
- Operational guidance to support Member States in preparing for and implementing COVID-19 vaccination
- Q&A on vaccination during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Guidance on routine immunization services during COVID-19 pandemic in the WHO European Region
- Mitigating the impact of COVID-19 on control of vaccine-preventable diseases: a health risk management approach focused on catch-up vaccination (2020)
Publications
 Guidelines for the care and treatment of persons diagnosed with chronic hepatitis C virus infection (2018)
More publications
Guidelines for the care and treatment of persons diagnosed with chronic hepatitis C virus infection (2018)
More publications
Multimedia
Prevent hepatitis. Act now.
Key partners
WHO Regional Office for Europe works with several key partners on activities related to hepatitis
Read more