Strengthening maternal and newborn health in eastern Europe by improving quality of care in primary health facilities
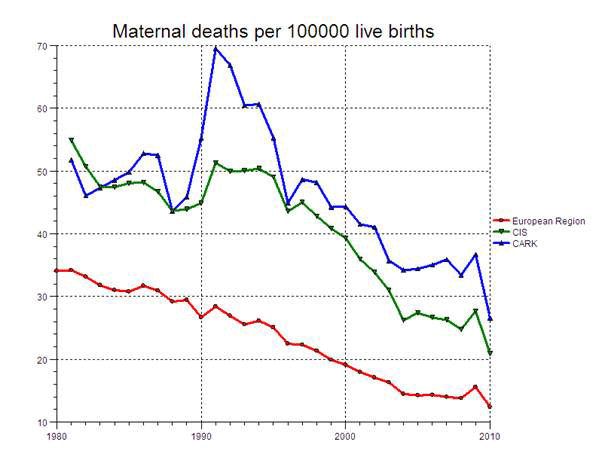
All 53 Member States in the WHO European Region have reduced maternal and newborn mortality (see figure from HFA DB). According to recent estimates from WHO, the United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF), the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA) and the World Bank, maternal mortality in the Caucasus and central Asian countries declined by an average of 2.1% from 1990 to 2010. Work must still be done for these countries to reach the 5.5% level required to achieve Millennium Development Goal (MDG) target 5A.
Essential interventions during pregnancy have proved to save the lives of women and newborn babies. These include: magnesium sulfate for eclampsia, antibiotics for premature rupture of membranes and corticosteroids to prevent respiratory distress syndrome in preterm babies.
High-quality primary health care is the key to reducing maternal and newborn morbidity and mortality. Recognizing the challenges that many countries face, the Government of the Russian Federation, in collaboration with WHO/Europe, has invested in a two-year project (2012–2013) to assist several countries to achieve MDGs 4 and 5 by improving primary health care for women and babies and the referral systems during pregnancy and after childbirth.
Objectives
To strengthen maternal and newborn health in primary health care facilities, international and national experts have agreed on the following aims:
- to improve the quality of health services for pregnant women, mothers and newborn babies consistent with evidenced-based practice in target countries;
- to assess the quality of maternal and newborn care in primary health care facilities and develop recommendations for further improvement;
- to expand the availability of Russian-speaking health care professionals to help countries use the tools for improving the quality of care at primary health care facilities;
- to invest in training of health care professionals and enhance the role of midwives;
- to further develop expertise in the European Region in assisting countries to improve their monitoring of progress in maternal and newborn health; and
- to establish a platform for the exchange of evidence and information among all countries in the eastern part of the Region.
Note: *CIS stands for Commonwealth of Independent States; CARK stands for central Asian republics and Kazakhstan.